 Did you know that understanding US customs duties could save you thousands of dollars on imports from China? Many importers overlook the importance of correctly calculating customs duties and taxes, leading to surprise costs that eat into profits. By mastering these essential details, not only can you reduce expenses, but you’ll also ensure compliance with US regulations and avoid costly delays. This guide will show you how to calculate these fees, avoid common mistakes, and implement strategies that keep your imports running smoothly while maximizing savings.
Did you know that understanding US customs duties could save you thousands of dollars on imports from China? Many importers overlook the importance of correctly calculating customs duties and taxes, leading to surprise costs that eat into profits. By mastering these essential details, not only can you reduce expenses, but you’ll also ensure compliance with US regulations and avoid costly delays. This guide will show you how to calculate these fees, avoid common mistakes, and implement strategies that keep your imports running smoothly while maximizing savings.
Customs Duties and Import Taxes Explained
What Are Customs Duties?
Customs duties are taxes imposed by a country on goods imported from abroad. These fees are applied to ensure fair competition with domestic products and generate revenue for the government. When you import products from China into the US, you are responsible for paying these duties.
Here are the most common types of duties you’ll encounter:
- Ad Valorem Duty: A percentage of the product’s value (e.g., 5% of total value).
- Specific Duty: A fixed fee based on the quantity or weight (e.g., $100 per ton).
- Compound Duty: A mix of ad valorem and specific duties (e.g., 2% of value + $50 per item).
Understanding how these are calculated can help you avoid unexpected costs and plan more efficiently for your imports.
Understanding Import Taxes
Besides customs duties, you also need to be aware of other import taxes that may apply, including tariffs, value-added tax (VAT), and sales tax. Each of these taxes impacts the total cost of your shipment differently:
- Tariffs: These are specific taxes imposed by governments to protect domestic industries. Since the US-China trade war, certain products face extra tariffs, ranging from 7.5% to 25%.
- Value-Added Tax (VAT): Though the US doesn’t impose VAT, many countries do. If you are exporting from China to other countries, be prepared for this additional tax that can vary between 5% to 20%.
- Sales Tax: Some US states apply sales tax to goods imported and sold locally, which varies depending on state laws.
| Tax Type | What It Applies To | When It Applies |
|---|---|---|
| Customs Duties | Imported goods | Based on HS code and product value |
| Tariffs | Specific goods (e.g., steel) | US-China trade conflict; extra duties on certain products |
| Sales Tax | Goods sold locally | Varies by state; paid at point of sale |
What Products Are Subject to Duties and Taxes?
Certain product categories are more likely to face high customs duties and taxes. Here are some of the key categories with elevated duty rates:
- Electronics: Laptops, smartphones, and other tech products.
- Textiles and Apparel: Clothing, fabrics, and accessories.
- Machinery: Industrial machinery and equipment.
- Automotive Parts: Car parts and accessories.
- Footwear: Shoes and related goods.
Understanding which products are subject to higher duty rates can help you plan better and minimize your total import costs.
2024 US-China Tariffs Overview
US-China Trade Relations Overview
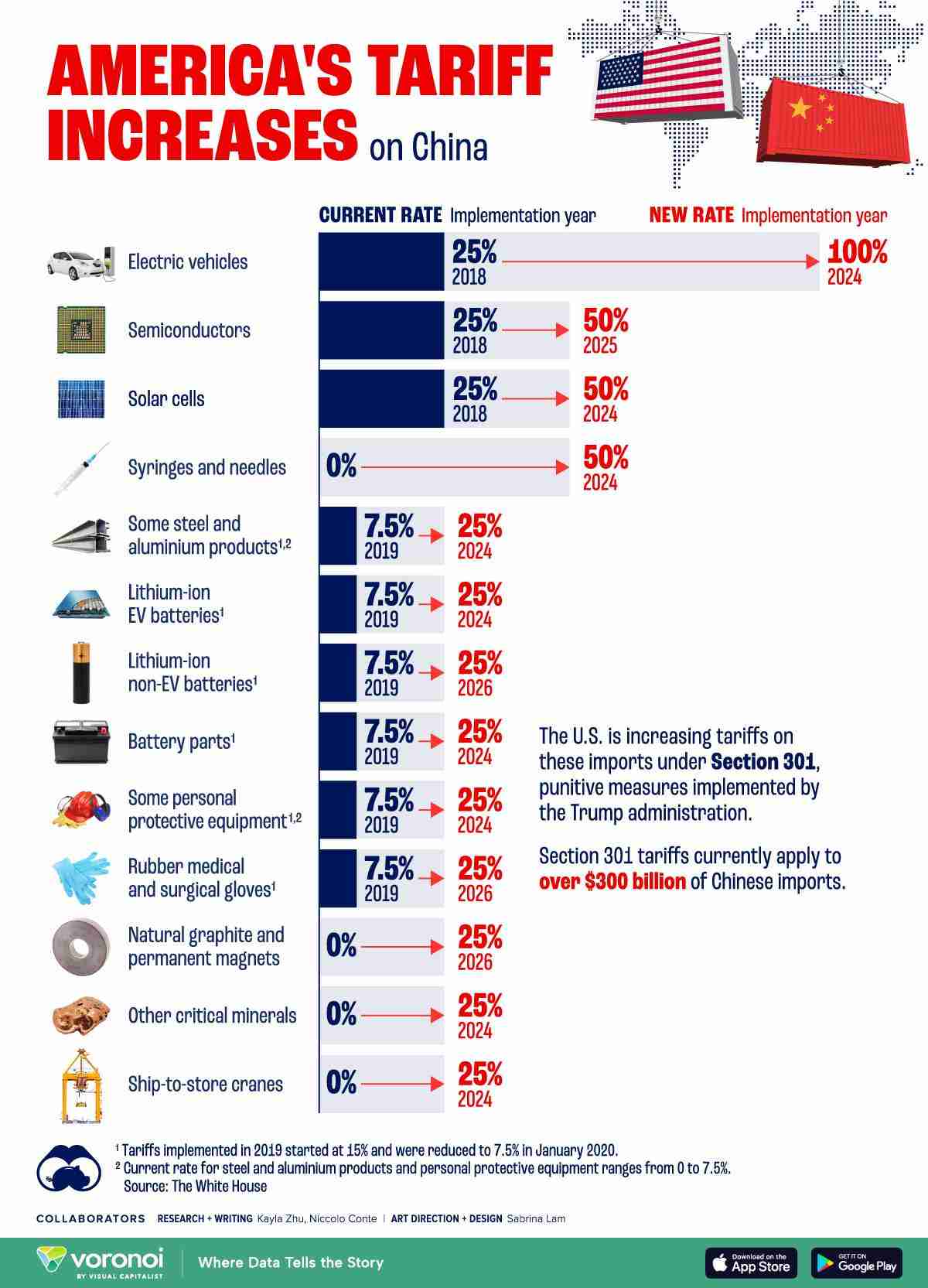
The trade tensions between the US and China have had a significant impact on global trade, particularly following the introduction of Section 301 tariffs in 2018. These tariffs were a response to China’s trade practices, including issues like intellectual property theft and forced technology transfers. The goal was to level the playing field for US companies, but it has added considerable costs for importers sourcing from China.
Key milestones:
- July 6, 2018: The US imposed tariffs on $34 billion worth of Chinese imports, marking the start of the trade war.
- August 23, 2018: A second round of tariffs targeted $16 billion in goods.
- September 24, 2018: The US expanded tariffs to cover $200 billion of Chinese imports, with initial rates set at 10% but later raised to 25%.
- January 15, 2020: A “Phase One” deal was signed, slightly reducing tariffs on some goods, but most tariffs remain in place as of 2024.
Today, the Section 301 tariffs continue to impact a wide range of Chinese products, driving up costs for US importers.
Current Tariffs by Product Category
As of 2024, tariffs remain in effect on a broad array of goods imported from China, affecting industries ranging from consumer electronics to machinery. Below is a breakdown of the current tariff rates on commonly imported products:
| Product Category | Tariff Rate in 2024 |
|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | 7.5% |
| Apparel and Footwear | 25% |
| Machinery and Equipment | 20% |
| Furniture | 10% |
| Automotive Parts | 25% |
For example, if you’re importing apparel, you’ll face a 25% tariff on top of other import costs, significantly increasing the final landed cost.
Section 301 Tariffs: Key Sectors Affected
The Section 301 tariffs specifically target industries that are critical to US-China trade. Here are the key sectors currently impacted:
- Technology and Electronics: Items like smartphones, laptops, and circuit boards are subject to a 7.5% tariff.
- Textiles and Apparel: Products such as clothing, fabrics, and shoes face the highest tariffs, typically around 25%.
- Industrial Machinery: Equipment used in construction, manufacturing, and agriculture is subject to tariffs as high as 20%.
- Furniture and Household Goods: Tariffs on items like furniture range from 10% to 25%, affecting home goods retailers significantly.
- Automotive Parts: Car components, including engines and transmissions, carry a 25% tariff, directly impacting the automotive repair and manufacturing sectors.
These tariffs continue to affect import costs in 2024, making it essential for businesses to carefully plan and account for these additional expenses when importing from China.
How to Calculate Customs Duties for Imports from China
Calculating customs duties can seem complicated, but breaking it down step by step will make it more manageable. Here’s how to do it correctly, so you can avoid surprises and overpaying on your imports from China.
Step 1: Identify the HS Code of Your Product

The first step to calculating customs duties is identifying the Harmonized System (HS) Code for your product. The HS Code is a universal system used to classify goods, and it’s crucial because it determines the duty rate for your item.
Here’s how to find it:
- Check with your supplier: Ask them to provide the correct HS Code for the goods.
- Use the USITC Tariff Database: Visit the U.S. International Trade Commission (USITC) website to search for your product’s HS Code.
- Consult a customs broker: If you’re unsure, a broker can help you classify the goods correctly.
Once you have the HS Code, you’re ready to move to the next step.
Step 2: Check the Tariff Rate
After you’ve identified the HS Code, the next step is to check the tariff rate associated with that code. The rate will vary depending on the product and whether it falls under additional tariffs like the Section 301 tariffs.
Here’s where to find the tariff rate:
- USITC Tariff Database: Go to the USITC website and search by HS Code to find the base tariff rate for your product.
- Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS): Use the HTS website, which provides up-to-date tariff rates and any special provisions.
- Check for Section 301 tariffs: If your product is subject to these tariffs, you’ll need to add the extra percentage (e.g., 7.5% or 25%).
Step 3: Calculate Customs Duties
 Once you know the tariff rate, calculating the duty is simple. Use the following formula:
Once you know the tariff rate, calculating the duty is simple. Use the following formula:
Customs Duty = Product Value x Tariff Rate
Here’s a step-by-step example:
- HS Code: Let’s say your product is classified under HS Code 9503.00.00 (toys).
- Product Value: Your shipment’s declared value is $10,000.
- Tariff Rate: The standard tariff for toys is 4.5%, and there are no additional tariffs.
Now, calculate the customs duty:
- Customs Duty = $10,000 x 4.5% = $450
So, you’ll pay $450 in customs duties for this shipment.
Example Table: Duty Calculation for Different Product Values
| Product Value | Tariff Rate | Customs Duty |
|---|---|---|
| $10,000 | 4.5% | $450 |
| $20,000 | 4.5% | $900 |
| $50,000 | 4.5% | $2,250 |
This simple table shows how the customs duty increases as the value of your shipment rises.
Step 4: Add VAT and Local Sales Tax (if applicable)
If you’re importing goods to a country that applies VAT (not the US), you’ll need to add this tax to your calculation. The US does not impose VAT, but some states apply local sales tax when goods are sold locally.
Here’s how to add VAT or sales tax:
- VAT: Let’s say you’re shipping to the EU, where the VAT is 20%. The VAT would be applied to the product value + customs duty.
- Sales Tax: Some US states charge sales tax based on the retail value of the goods once they are sold.
For most US imports, you won’t deal with VAT, but local sales tax may come into play when you sell the goods in certain states.
Bonus: To simplify your duty calculations, consider using a Customs Duty Calculator. Many online tools allow you to input your product value and HS Code, and they’ll calculate the duties for you automatically.
The US Customs Clearance Process
Navigating the US customs clearance process can be challenging, but understanding the key steps and documents required will help you avoid delays and costly mistakes. Let’s break down what you need to know.
Required Documentation
To clear customs smoothly, having the correct documents is non-negotiable. Missing or incorrect paperwork is one of the main reasons for shipment delays. Here’s a list of essential documents you need:
 Commercial Invoice: This document includes details about the buyer, seller, shipment, and the total value of goods. It’s crucial for calculating duties and taxes.
Commercial Invoice: This document includes details about the buyer, seller, shipment, and the total value of goods. It’s crucial for calculating duties and taxes.- Packing List: Lists all the items in your shipment, including descriptions, weights, and dimensions. Customs uses this to verify the contents of your shipment.
- Bill of Lading: This is the contract between you and the freight carrier. It serves as proof that the carrier has received the goods and agrees to deliver them to the destination.
- Arrival Notice: Notifies the consignee that their goods have arrived and are awaiting customs clearance.
Pro Tip: Double-check your documents for accuracy, especially the product values on your commercial invoice. Customs authorities will scrutinize these numbers.
Working with a Customs Broker
Hiring a customs broker can make the customs clearance process much easier, especially if you’re dealing with large or complex shipments. Here are the main benefits:
- Expertise: Brokers are well-versed in tariff classifications, regulations, and how to correctly file documentation. This ensures faster and smoother clearance.
- Avoid Mistakes: A broker can help you avoid costly errors, such as misclassifying goods or submitting incomplete paperwork.
- Time-Saving: Customs clearance can be time-consuming. A broker takes care of the process, allowing you to focus on other areas of your business.
- Compliance: Brokers help ensure you stay compliant with US regulations, reducing the risk of penalties and shipment holds.
US Customs Inspection Process
Once your shipment arrives in the US, it goes through customs inspection. Here’s a breakdown of how that works:
- Document Review: Customs officers first check the required documents to ensure everything is in order (commercial invoice, bill of lading, etc.).
- Cargo Examination: In some cases, customs may physically inspect your goods. This can happen randomly or if your shipment is flagged for any discrepancies.
- Release or Hold: If everything checks out, your shipment is released. If there are issues (e.g., incorrect paperwork or suspicious cargo), the shipment will be held until they are resolved.
- Customs Duty Payment: After the inspection, any applicable customs duties and taxes must be paid before the goods are fully released.
Pro Tip: Always ensure your documentation matches the actual shipment. Discrepancies can lead to delays, fines, or even confiscation of goods.
The US Customs Clearance Process
Navigating the US customs clearance process can be challenging, but understanding the key steps and documents required will help you avoid delays and costly mistakes. Let’s break down what you need to know.
Required Documentation
To clear customs smoothly, having the correct documents is non-negotiable. Missing or incorrect paperwork is one of the main reasons for shipment delays. Here’s a list of essential documents you need:
- Commercial Invoice: This document includes details about the buyer, seller, shipment, and the total value of goods. It’s crucial for calculating duties and taxes.
- Packing List: Lists all the items in your shipment, including descriptions, weights, and dimensions. Customs uses this to verify the contents of your shipment.
- Bill of Lading: This is the contract between you and the freight carrier. It serves as proof that the carrier has received the goods and agrees to deliver them to the destination.
- Arrival Notice: Notifies the consignee that their goods have arrived and are awaiting customs clearance.
Pro Tip: Double-check your documents for accuracy, especially the product values on your commercial invoice. Customs authorities will scrutinize these numbers.
Working with a Customs Broker
Hiring a customs broker can make the customs clearance process much easier, especially if you’re dealing with large or complex shipments. Here are the main benefits:
- Expertise: Brokers are well-versed in tariff classifications, regulations, and how to correctly file documentation. This ensures faster and smoother clearance.
- Avoid Mistakes: A broker can help you avoid costly errors, such as misclassifying goods or submitting incomplete paperwork.
- Time-Saving: Customs clearance can be time-consuming. A broker takes care of the process, allowing you to focus on other areas of your business.
- Compliance: Brokers help ensure you stay compliant with US regulations, reducing the risk of penalties and shipment holds.
US Customs Inspection Process
Once your shipment arrives in the US, it goes through customs inspection. Here’s a breakdown of how that works:
- Document Review: Customs officers first check the required documents to ensure everything is in order (commercial invoice, bill of lading, etc.).
- Cargo Examination: In some cases, customs may physically inspect your goods. This can happen randomly or if your shipment is flagged for any discrepancies.
- Release or Hold: If everything checks out, your shipment is released. If there are issues (e.g., incorrect paperwork or suspicious cargo), the shipment will be held until they are resolved.
- Customs Duty Payment: After the inspection, any applicable customs duties and taxes must be paid before the goods are fully released.
Pro Tip: Always ensure your documentation matches the actual shipment. Discrepancies can lead to delays, fines, or even confiscation of goods.
Strategies to Minimize Customs Duties and Taxes
Importing goods from China to the US doesn’t always have to come with high customs duties and taxes. There are several smart strategies you can use to reduce these costs and boost your profit margins. Let’s dive into the most effective methods.
Free Trade Agreements and Tariff Exemptions
One of the easiest ways to lower import costs is to take advantage of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) and tariff exemptions. In 2024, there are several exemptions that might apply depending on your product type and origin.
Here are a few key exemptions to consider:
- Generalized System of Preferences (GSP): While China doesn’t benefit from this, importing from other countries might lower or eliminate duties.
- Product-Specific Tariff Exemptions: Certain goods may qualify for tariff reductions or exemptions due to specific trade deals or special programs.
- Section 301 Exclusions: Keep an eye on any exclusions related to the ongoing US-China trade tariffs. Sometimes, product-specific exemptions are issued, which could mean zero tariffs on specific imports.
Optimizing Shipping Methods
Your shipping method can also play a huge role in minimizing customs duties and fees. Here are a couple of tactics to consider:
- Consolidated Shipping: When you group smaller shipments into one larger container (LCL – Less-than-Container Load), it helps reduce overall shipping fees. Consolidation allows you to split the customs duty costs with others shipping similar goods.
- De Minimis Value Rule: Shipments valued at $800 or less enter the US duty-free under the De Minimis rule. If your goods fall under this threshold, you can avoid paying customs duties altogether.
Leveraging Free Trade Zones (FTZ)
Another highly effective strategy to reduce or delay customs duties is to use a Free Trade Zone (FTZ). FTZs allow businesses to import goods, store them without paying duties, and either re-export them or delay duty payment until they leave the zone.
Here’s how an FTZ works:
- Import goods into the FTZ without paying any duties.
- Store or assemble products within the zone. You can even repackage or reclassify products.
- Re-export goods without paying duties, if they are not entering the US market.
- If you choose to sell them in the US later, you pay the duties only when the goods leave the FTZ.
This strategy is especially useful if you’re uncertain about immediate sales or if you plan to re-export part of your inventory.
Pro Tip: Some FTZs also allow duty deferral on products that are assembled or transformed in the zone.
Reclassifying Products
Reclassifying your goods under a different HS Code can potentially reduce the duties you owe. However, this needs to be done legally and strategically. Here’s how you can go about it:
- Step 1: Review your product’s current HS Code classification.
- Step 2: Consult a customs broker to identify if a different classification may apply that offers a lower tariff rate.
- Step 3: Submit a binding ruling request to the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) to get official approval for the reclassification.
- Example: A company importing parts might reclassify them under components instead of fully assembled products, which can often lower duty rates.
By understanding and applying these strategies, you can effectively minimize your import costs, keeping more money in your business while ensuring compliance with US regulations.
FAQs on Import Taxes and Duties from China to the USA
What are US customs duties and how are they calculated?
US customs duties are taxes imposed on goods imported into the United States from other countries, including China. These duties are calculated based on the product's value, its classification under the Harmonized System (HS) Code, and the applicable tariff rate. The tariff rate is determined by the product category and may include additional tariffs, such as those imposed under the Section 301 tariffs.
What is the difference between customs duties and tariffs?
Customs duties are the broader category of taxes imposed on imports, which can include various types of charges such as ad valorem duties (a percentage of the product's value) and specific duties (a fixed amount based on quantity or weight). Tariffs, on the other hand, are specific taxes or duties that are often applied to protect domestic industries or as a result of trade disputes, like the US-China trade war. Tariffs are one type of customs duty.
How can I reduce customs duties on goods imported from China?
There are several strategies to reduce customs duties, including leveraging Free Trade Zones (FTZs) to delay or eliminate duty payments, reclassifying products under HS Codes with lower tariff rates, and taking advantage of any applicable tariff exemptions or free trade agreements. Optimizing shipping methods, such as consolidated shipping, can also help reduce overall fees. In some cases, ensuring that the value of shipments remains under the de minimis threshold can help avoid duties altogether.
What documents are required for US customs clearance?
To clear customs in the United States, you will need several essential documents. These include the commercial invoice, which details the value and nature of the goods, the packing list that provides a breakdown of the shipment’s contents, and the bill of lading, which serves as the contract between the shipper and carrier. Other documents, such as the arrival notice and any permits required for restricted goods, may also be necessary.
What happens if my shipment is held by US customs?
If your shipment is held by US customs, it could be due to missing or incorrect documentation, suspicion of incorrect product classification, or a random inspection. In this case, customs officials will either request additional information or conduct a physical inspection of the goods. Depending on the issue, the shipment could be delayed for a few days to several weeks. Once the issue is resolved and any required duties are paid, the goods will be released.
Final Thoughts and Next Steps
Navigating US customs duties and import taxes from China can be complex, but by understanding the process and applying the right strategies, you can save on costs and avoid common pitfalls. Here’s a recap of the most important takeaways from this guide, along with actionable next steps to ensure smooth importing.
Recap Key Points
Understanding the following points will help you optimize your importing process:
- Identify the correct HS Code for your product to ensure accurate duty calculations.
- Be aware of the Section 301 tariffs, which can significantly increase the cost of certain imports from China.
- Use Free Trade Zones (FTZs) to delay or eliminate duty payments, especially for goods that will be re-exported.
- Reclassifying products under a different HS Code can help reduce customs duties, but make sure to follow legal guidelines and consult experts when necessary.
- Ensure all required documentation is accurate and complete to avoid delays or penalties at customs.
Next Steps
To further streamline your importing process and reduce costs, here’s what you should do:
- Consult a customs broker: A broker can help you navigate complex duties, tariffs, and paperwork, ensuring compliance and minimizing errors.
- Calculate duties before shipping: Use available tools, such as a Customs Duty Calculator, to estimate your duties based on product value and HS Code.
- Research product-specific tariffs: Stay updated on the latest tariffs affecting your goods, especially if they fall under categories with additional duties, like electronics or textiles.
Final Additions
Here are some additional resources to further assist you:
Internal Links
External Links
- US Customs and Border Protection (CBP) Website: CBP.gov
- Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS): HTS Website
- USITC Tariff Database: USITC.gov
By following these steps and utilizing these resources, you’ll be better equipped to handle the complexities of importing from China, minimizing your costs, and ensuring smooth customs clearance.


 Commercial Invoice: This document includes details about the buyer, seller, shipment, and the total value of goods. It’s crucial for calculating duties and taxes.
Commercial Invoice: This document includes details about the buyer, seller, shipment, and the total value of goods. It’s crucial for calculating duties and taxes.









